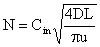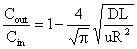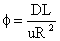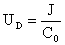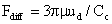
















|
|
Particle Deposition Mechanisms: Mass Diffusion Tube Deposition Consider a constant velocity gas flow in a tube of length L and radius R. The residence time is t = L/u where u is the gas velocity. Assuming that the wall deposition process is similar to that of a uniform concentration near a wall, and using (20) it follows that
or
A detailed duct flow analysis shows
Diffusion Velocity The diffusion velocity is defined as
Similarly, a diffusion force may be defined as
|


|