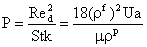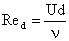|
Particle Deposition Mechanisms: Impaction
Impaction of Non-Stokesian Particles
The equation of motion of a particle is given as
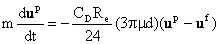
|
(10)
|
where
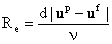
|
(11)
|
and 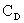 is a drag
coefficient. Equation (10) may be restated in non-dimensional form as is a drag
coefficient. Equation (10) may be restated in non-dimensional form as

|
(12)
|
Numerical solutions for inviscid flows around cylinders and spheres were
obtained by Brun et al. (1955) and Dorsch et al. (1955).
The results depend on Stk and parameter P given as
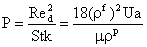
|
(13)
|
where the particle Reynolds number is defined as
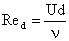
|
(14)
|
Variations of capture efficiency with Stokes number for different values
of P were given by Frielander (2000). See also Figure 1 (next page). | 

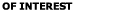




















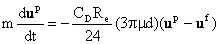
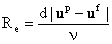
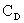 is a drag
coefficient. Equation (10) may be restated in non-dimensional form as
is a drag
coefficient. Equation (10) may be restated in non-dimensional form as