|
Colloids
Electrical Double Layer Interactions for Colloidal Systems
Most colloidal particles carry electrostatic charges. Since the
dispersion as a whole is neutral, there must be an excess of ions of opposite
charge in the solution. These excess ions are found near the surface of
suspended colloidal particles and form what is called a "diffused electrical
double layer." The double layer has a profound effect on interactions of
colloidal particles.
Ion Distribution Near a Colloidal Particle
Consider the diffusion of ions near a charged surface. The convective
diffusion equation for the number concentration,  is given as is given as

|
(1)
|
where 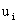 is the
velocity due to the electric field. Force balance of a single ion gives is the
velocity due to the electric field. Force balance of a single ion gives

|
(2)
|
where E is the electric field strength given as

|
(3)
|
and 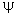 is the electric field potential. is the electric field potential.
Equation (2) leads to

|
(4)
|
where
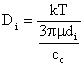
|
(5)
|
is used. Using (3) and (4) in (1), we find

|
(6)
|
or
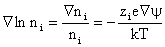
|
(7)
|
Integrating (7), one finds

|
(8)
|
the well-known Boltzmann distribution. Note that the
potential  . .
Using Coulomb's law and equation (3), we find

|
(9)
|
where  is the
charge density given as is the
charge density given as

|
(10)
|
Using (10) in (9), the Poisson-Baltzamann equation follows, i.e.

|
(11)
|
Solution of (11) gives  .
Equation (11) is restricted to low electrolyte concentrations, since ions are
treated as point charges. .
Equation (11) is restricted to low electrolyte concentrations, since ions are
treated as point charges.
|
























 is given as
is given as 
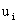 is the
velocity due to the electric field. Force balance of a single ion gives
is the
velocity due to the electric field. Force balance of a single ion gives


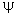 is the electric field potential.
is the electric field potential.

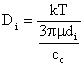

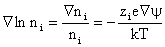

 .
.

 is the
charge density given as
is the
charge density given as


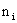 .
Equation (11) is restricted to low electrolyte concentrations, since ions are
treated as point charges.
.
Equation (11) is restricted to low electrolyte concentrations, since ions are
treated as point charges.