

















|
|
Reynolds Equation and Mixing Length Model Phenomenological Theories of Turbulence Logarithmic Velocity Near a Wall Very near wall, in the viscous sublayer, turbulence fluctuation becomes small and the viscous stress becomes dominant. As a result,
or
Hence,
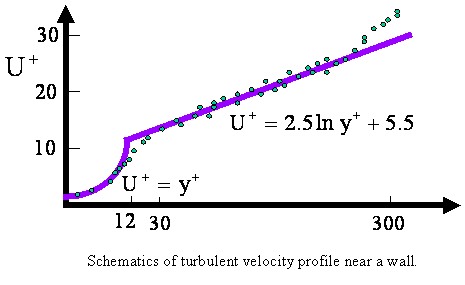
A schematic of the velocity profile is shown in the figure. Reichardt
suggested a smooth curve for the buffer region (Schlichting, McGraw-Hill, 1960). Outside
the viscous sublayer approximate expressions given by
|


|


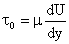
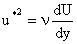 ,
,
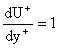
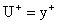 ,
(
,
( 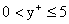 ),
),
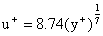 and
and
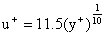 may be used.
may be used.