



















|
|
Features of Turbulence Kolmogorov Inertia Subrange Spectrum For eddies much smaller than the energy containing eddies and
much larger than dissipative eddies (of the order of Kolmogorov scales),
turbulence is controlled solely by the dissipation rate
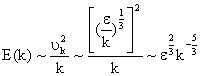
which is the famous -5/3 law of Kolmogorov. In the derivation of (8), simple
dimensional argument is used and velocity scale of eddies of size
( The process of energy cascade in turbulence is summarized by Richardson verse: "Big whirls have little whirls that feed on their velocity. Little whirls have lesser whirls, and so on to viscosity." |


|


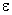 and the
size of the eddy (
and the
size of the eddy ( 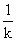 ). In this subrange,
). In this subrange,
 ,
,
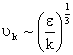 is used.
is used.