 |
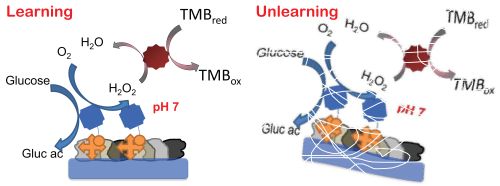
We report a realization of an
associative memory signal/information processing system based on simple
enzyme-catalyzed biochemical reactions. Optically detected chemical
output is always obtained in response to the triggering input, but the
system can also “learn” by association, to later respond to the second
input if it is initially applied in combination with the triggering
input as the “training” step. This second chemical input is not
self-reinforcing in the present system, which therefore can later
“unlearn” to react to the second input if it is applied several times
on its own. Such processing steps realized with (bio)chemical-kinetics
promise applications of bio-inspired/memory-involving components in
“networked” (concatenated) biomolecular processes for multi-signal
sensing and complex information processing.
V. Bocharova, K. MacVittie, S.
Chinnapareddy, J. Halámek, V.
Privman, E. Katz, Realization of associative memory in an enzymatic
process: Toward biomolecular networks with learning and unlearning
functionalities. J. Phys. Chem. Lett.
2012, 3, 1234-1237.
|
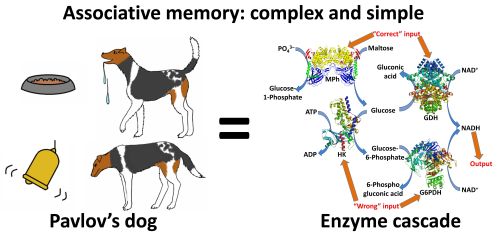 |
A biomolecular system representing
the first realization of associative memory based on enzymatic
reactions in vitro has been designed. The system demonstrated
“training” and “forgetting” features characteristic of memory in
biological systems, but presently realized in simple biocatalytic
cascades.
K. MacVittie, Jan Halámek,
V. Privman, E. Katz, A
bioinspired associative memory system based on enzymatic cascades. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6962-6964.
|
Updated on November 16, 2013
