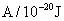|
London-van der Waals Force
Hamaker Constants for Dissimilar Materials
Tables 5 and 6 gives the values of Hamaker constant for a number
materials in vacuum and in water.
Table 5. Values of Hamaker Constant for some materials.
|
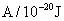
|
|
Materials |
Vacuum |
Water |
|
Polystyrene |
7.9 |
1.3 |
|
Hexadecane |
5.4 |
- |
|
Gold |
40 |
30 |
|
Silver |
50 |
40 |
|
Al2O3 |
16.75 |
4.44 |
|
Copper |
40 |
30 |
|
Water |
4.0 |
- |
Table 6. Values of Hamaker Constant for some materials.
|
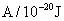
|
|
Materials |
Vacuum |
Water |
|
Pentane |
3.8 |
0.34 |
|
Decane |
4.8 |
0.46 |
|
Hexadecane |
5.2 |
0.54 |
|
Water |
3.7 |
- |
|
Quartz (Fused) |
6.5 |
0.83 |
|
Quartz (Crystalline) |
8.8 |
1.70 |
|
Fused Silica |
6.6 |
0.85 |
|
Calcite |
10.1 |
2.23 |
|
Calcium Fluoride |
7.2 |
1.04 |
|
Sapphire |
15.6 |
5.32 |
|
Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) |
7.1 |
1.05 |
|
Poly (Vinyl Chloride) |
7.8 |
1.30 |
|
Polyisoprene |
6.0 |
0.74 |
|
Poly (tetrafluoroethylene) |
3.8 |
0.33 |
|