



















|
|
Reynolds Equation and Mixing Length Model Equation (10) is referred to as the Reynolds equation. The term
Equation (10) may be restated as
where The Reynolds stress (turbulent stress) is a symmetric tensor and its components are given by
Note that the turbulent stresses introduce six additional unknowns into the averaged Navier-Stokes equation. |


|


 is the stress induced by the turbulent fluctuation. i.e.,
is the stress induced by the turbulent fluctuation. i.e.,
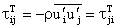

 is the
mean viscous stress tensor and
is the
mean viscous stress tensor and 