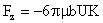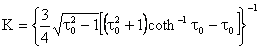



















|

|
| Viscous Flows | |
| Navier-Stokes Equation, Vorticity, Stream Function | Exact Solutions | Drag on Spherical Particles | Creeping Flows | Nonspherical Particles | |
|
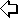
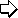
Hydrodynamic Forces and Torques for a Nonspherical Particle Prolate Spheroid Translating in a Quiescent Fluid The motion of a rigid prolate spheroid parallel to its axis of revolution as shown in
Figure 4 is studied in this section. The appropriate coordinates system for this problem
is the prolate coordinate system
Figure 4. Schematic of a prolate spheroids in creeping flow motion. For convenience, we let
The surface
and
Similar to the method used for the oblate spheroid, one can solve the equation of creeping motion in prolate spheroidal coordinates subject to appropriate boundary conditions. The stream function for a prolate spheroid translating with velocity U in the positive z-direction parallel to its axis of revolution is given as
Using this expression in Equation (8), one obtains the force acting on the prolate spheroid, that is
where
and Equation (47) may be restated as
where the shape factor k is given by
|


|
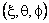 with
with
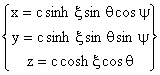
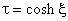
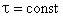 .
(
.
(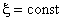 ) are prolate spheroids.
Then
) are prolate spheroids.
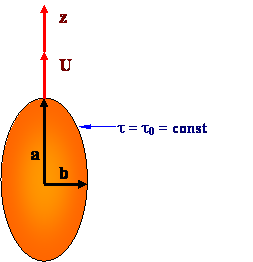
Then 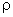 and z may be expressed as
and z may be expressed as

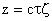
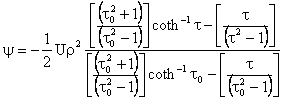
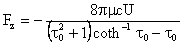
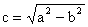
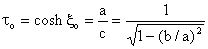 .
.