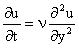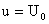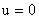



















|

|
| Viscous Flows | |
| Navier-Stokes Equation, Vorticity, Stream Function | Exact Solutions | Drag on Spherical Particles | Creeping Flows | Nonspherical Particles | |
|
|
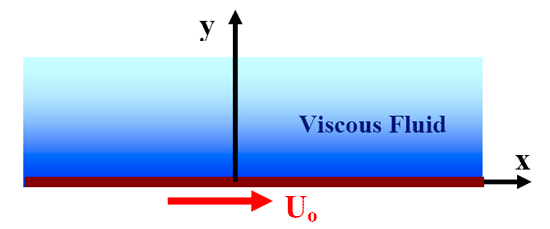
Exact Solutions to the Navier-Stokes Equation Unsteady Parallel Flows (Plate Suddenly Set in Motion) Consider that special case of a viscous fluid near a wall that is set suddenly in motion as shown in Figure 1. The unsteady Navier-Stokes reduces to
Figure 1. Schematics of flow near a wall suddenly set in motion. The boundary conditions are:
The corresponding initial condition for the fluid that starts from rest is given as
|


|