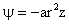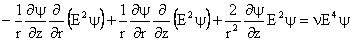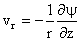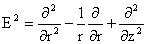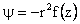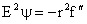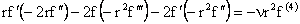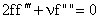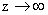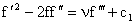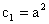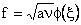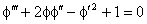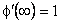



















|

|
| Viscous Flows | |
| Navier-Stokes Equation, Vorticity, Stream Function | Exact Solutions | Drag on Spherical Particles | Creeping Flows | Nonspherical Particles | |
|
|
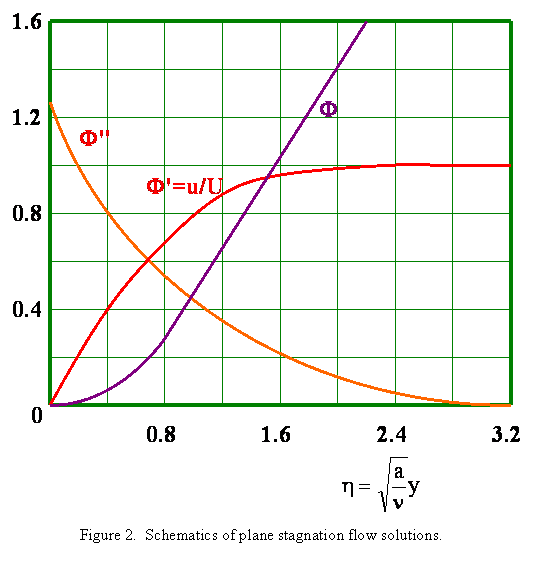
Incompressible Viscous Flows Plane Stagnation Flows
Potential axisymmetric stagnation flow is described as
The steady state Navier-Stokes equation for axisymmetric flows is given as
where
Similar to the plane flow case we look for a solution of the form
with
Using (25) and (26), Equation (22) reduces to
or
The boundary conditions are
or
Integrating (28) we find
For equation (31) to be valid at large z,
Introducing a change of variables
Equation (31) becomes
subject to
The numerical solutions of the flow filed are very similar to the plane stagnation flow case shown in Figure 2 with a slightly fuller velocity profile. The details of the numerical solution are discussed by Schlichting (1960). |


|