|
Particle Equation of Motion (BBO-Equation)
The general equation of motion of a small spherical particle
suspended in fluid is given as
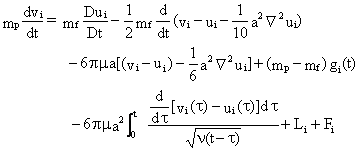
|
(1)
|
where
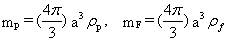 , ,
- a is the radius of the spherical particle,
- vi is the particle velocity,
- ui[y(t),t] is the fluid velocity at the particle location,
- μ is the viscosity,
- υ is the kinematic viscosity,
- ρp is the particle density,
- ρf is the fluid density,
- gi(t) is the acceleration of gravity, and
- y(t) is the location of the particle.
Saffman's (1965, 1968) lift force Li and
the acoustical force Fi are added to Equation (1) for completeness.
|