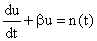|
Brownian Motions
When a small particle is suspended in a fluid, it subjected to
the impact gas or liquid molecules. For ultra fine
particles (colloids), the instantaneous momentum imparted to
the particle varies random which causes the particle to move on
an erratic path now known as Brownian motion.
Figure 1 illustrates the Brownian motion process.

Figure 1. Schematics of a Brownian motion process.
The Brownian motion of a small particle in a stationary
fluid in x-direction is governed by the following Langevin equation,
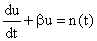
|
(1)
| where u is the velocity of the particle,
|
|
| Brownian Motion Calculation Models |
 |
Brownian Motion - Introductory
Spherical particle motion in poiseuille flow with brownian effects...
Brownian Motion - Advanced
Spherical particle motion in poiseuille flow with brownian effects... |
 |
|


















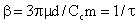
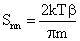
 is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature. It should be emphasized
that the Brown motion occurs in three dimensions and Equation (1) applies only
to the x-component of the motion.
is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature. It should be emphasized
that the Brown motion occurs in three dimensions and Equation (1) applies only
to the x-component of the motion.
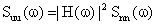
 is
the power spectrum of the velocity of the Brownian particle, and
is
the power spectrum of the velocity of the Brownian particle, and
 is the system function given by
is the system function given by