

















|
|
Particle Deposition Mechanisms: Mass Diffusion Effect of Mass The diffusivity as given by (3) and (4) is independent of particle density, but heavy particles do not respond swiftly to the molecular impacts. A time dependent analysis leads to
where Aerosol Mean Free Path The apparent mean free path for aerosol particles
|


|


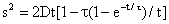
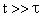 , (10)
reduces to Equation (5).
, (10)
reduces to Equation (5).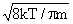 .
From the definition of stop distance it follows that
.
From the definition of stop distance it follows that

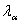 is of
the order of 10-6 cm for d < 5 μ.
is of
the order of 10-6 cm for d < 5 μ.