|
Ellipsoidal Particles
For particles that are ellipsoids of revolution, the drag force is given by
where a is the equatorial semi-axis of the ellipsoids and K′ is a shape factor.
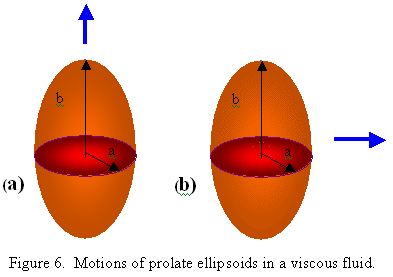
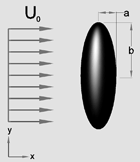
For the motion of a prolate ellipsoid along the polar axis as shown in Figure 6a,
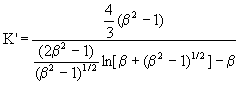 |
|
(18) |
where β is the ratio of the major axis b to the minor axis a.
For the motion of a prolate ellipsoid of revolution transverse
to the polar axis, as shown in Figure 6b
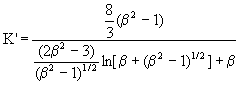
| |
(19) |
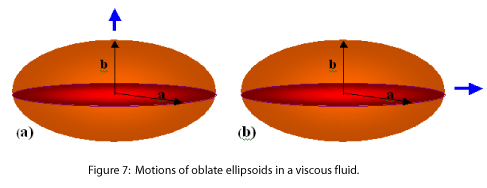
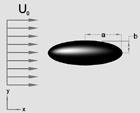
Similarly, for the motion of an oblate ellipsoid of revolution
along the polar axis as shown in Figure 7a,
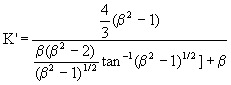
| |
(20) |
|
|
| Calculation Models - Ellipsoids of Revolution |
 |
Oblate Ellipsoid - Shape Factor
Prolate Ellipsoid - Shape Factor
|
 |
|