

















|
Electrodynamics Aerosols Charging and Their Kinetics Most aerosol particles carry some electrical charges. In an electric field of strength E, a charged particle experiences a force, which is given by
Here
where e is the elementary unit of charge and Particle Mobility Particle mobility is defined as the velocity that it will acquire when subjected to an electric field of unit strength. Equating the drag and Columbic forces, it follows that
For
Particle Charging Aerosol particle can be electrified by a number of different processes. Among the important ones are: Direct ionization, static electrification, electrolytic effects (liquids of high dielectric constant exchange ions with metals), contact electrification, spray electrification, frictional electrification, collisions with ion, diffusion, and field charging. Boltzmann Equilibrium Charge DistributionUnder equilibrium conditions, the aerosols approach the Boltzmann charge distribution. Accordingly, the fraction of particles having
For
For a room temperature of
The average number of charge per particle is given by
Electric Field of a Point Charge The electric field strength of a point charge at a distance r is given by
where |


|


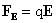 . (4)
. (4)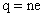 (5)
(5)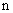 is the number of elementary units carried by the particle. (
is the number of elementary units carried by the particle. (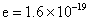 coulombs (MKS)=
coulombs (MKS)= 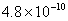 Statcoulombs (electrostatic cgs unit).)
Statcoulombs (electrostatic cgs unit).)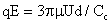 (6)
(6)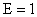 , the mobility becomes
, the mobility becomes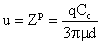 (7)
(7)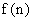 , is given by
, is given by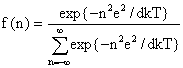 . (8)
. (8) , the approximate expression for the charge distribution becomes
, the approximate expression for the charge distribution becomes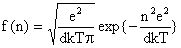 . (9)
. (9) , (9) reduces to
, (9) reduces to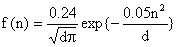
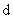 in
in 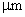 for
for 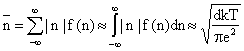 for
for 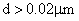 . (11)
. (11)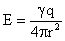 , (12)
, (12)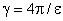 for cgs or electrostatic unit with
for cgs or electrostatic unit with 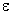 being the dielectric constant of the medium. For air,
being the dielectric constant of the medium. For air, 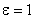 ,
, 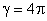 , and
, and 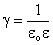 (for MKS).
(for MKS).